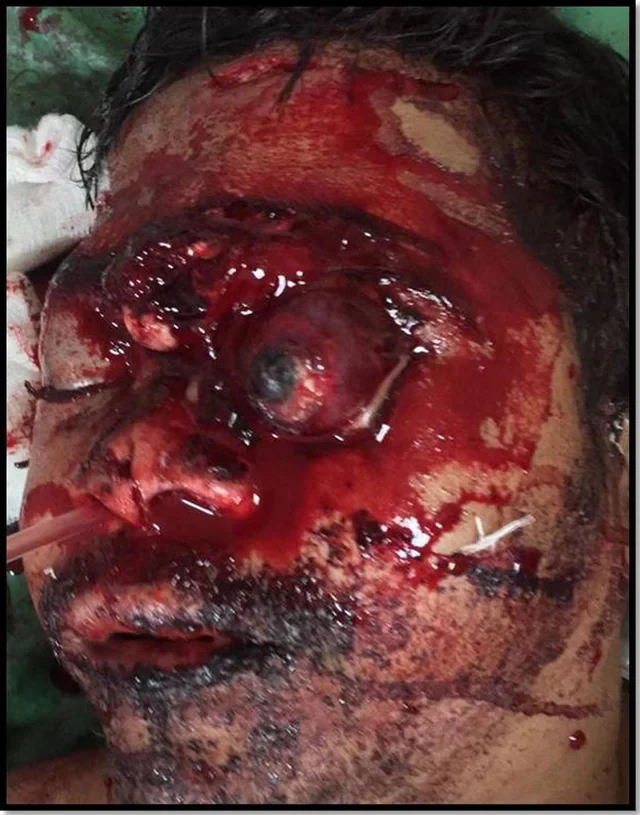
Image 1: Left sided eyeball subluxation and extensive craniofacial injury.
Image 2: Stepwise evacuation of retro-orbital hematoma. (a) Muscle identification and tagging. (b) Lateral canthotomy and inferior cantholysis. (c) Palpating optic nerve and orbital contents. (d) Orbital hematoma removal.
Image 3: Steps for globe reposition. (a) Ocular surface covered with amniotic membrane graft. Upper lid blepharotomy to lengthen anterior lamella and facilitate lid closure. (c) Placing Symblepharon ring. (d) Using symblepharon ring to mobilize globe and slip it under the upper lid.
Image 4: Surgical repair of craniofacial trauma. (a) Fixing palatal split. (b) Frontal fracture with CSF. (c) Harvesting Tensor fascia lata for dural repair. (d) On table outcome after tarsorrhaphy and wound closure.
Image 5: (a) Post operative appearance after 2 months. (b) Left eye prephthisical. Wound dehiscence of lower lid laceration repair.











 Slavshit
Slavshit

 Sandshit
Sandshit

Jump in the discussion.
No email address required.
21-year-old male was brought to the emergency department of our institute, with history of fall from a 2 wheeler bike and direct trauma to the forehead after hitting a roadside boulder. Patient was under the influence of alcohol and was not wearing a helmet. On admission patient's GCS (Glasgow Coma Scale) was 8/15.
Patient had sustained deep lacerated wounds on face, nose, left brow and forehead. There was CSF leak from the forehead wound. Left eye ball was luxated out of the socket beyond the equator (Fig. 1). There was no perception of light. The cornea appeared Edematous and showed a central 7 mm epithelial defect. There was no ocular motility. Pupils and anterior segment details could not be assessed due to corneal haziness. There was complete loss of conjunctiva. Medially a full-thickness lower lid laceration was identified. Both upper and lower lids were pushed behind the globe. The intraocular pressure was felt to be within normal limits digitally and the globe was intact. The contralateral eye was within normal limits. There were lacerated wounds in the occipital region, brow, forehead and on the dorsum of the nose up to the supratip. Clinically there was a floating maxilla with a mid palatal split. The midface was retro-displaced and there was derangement in occlusion. There was history of oral and nasal bleed. Computerized tomography (CT SCAN) imaging showed an intact but stretched optic nerve and hemorrhage behind the globe. A subgaleal hematoma was noted in the right occipital region. There was bifrontal fracture with involvement of both the inner and outer table of the frontal sinus on the left side. The displaced fracture fragment of the frontal bone had migrated intracranially (Fig. 2). Minimal frontal extradural hemorrhage was seen on the left side. Facial fractures included gross comminuted of the midface, nasal bone, lamina papyracea, medial and lateral orbital wall fractures on the right as well as left side.
After stabilizing vitals, initial suturing and dressing was done under local anesthesia. The lacerated wounds on the glabella and forehead were sutured. Lateral canthotomy and cantholysis was done to release intraorbital pressure and drain the retro orbital hemorrhage. An attempt to close the lids and repost the eyeball was made. Failing this, the protruded eyeball was protected by wet preserved amniotic membrane graft as a biological dressing till definitive surgery was undertaken. Sterile stainless steel surgical bowls were taped across the eye to offer protection from mechanical injury and contamination during oro-facial wound handling and dressing. Local antibiotics, steroids and lubricant drops were instilled.
Forty-eight hours later, patient was taken up for surgery with a multispeciality team comprising of maxillofacial, oculoplasty and neuro- surgeons.
The orbit was examined and the old semi dissolved amniotic membrane dressing was removed. All four recti muscles were hooked and tagged (Fig. 3a). The lateral canthotomy and cantholysis was extended and retro orbital contents palpated (Fig. 3b and c). After localizing and safeguarding the optic nerve, a suction catheter was introduced to evacuate the hemorrhage. However, it was found to be a well organized hematoma so the blood clots were removed piecemeal (Fig. 3d). There after, the ocular surface was covered by a fresh wet amniotic membrane (Fig. 4a). Lid crease incision and upper lid partial blepharotomy was performed to facilitate easy mobilizing of eyelid over the globe (Fig. 4b). A symbleparon ring was placed and the eyeball was gently slid under upper lid, followed by lower lid (Fig. 4c and d). Suture tarsorraphy was done maintain the postion of the globe. The lower lid laceration was then addressed and layered closure was done. The maxillofacial repair was then carried out (Fig. 5a).
Bilateral vestibular incision given, 2 L shaped plates fixed in right and left zygomatic buttress after reducing the midpalatal split and fixation of split with plate. Bilateral fronto zygomatic fracture and frontonasal fractures were exposed and plated. The frontal fracture was tackled in conjunction with the neurosurgical team. Minimal handling of the dorsum of nose and displaced frontal bone was done since the upper central block (frontal bone fragment) was deeply impacted with fractures extending up to the sphenoidal sinus. Considering the fact that gross mobilization may worsen the brain injury, minimal mobilization was done and CSF leak sealed with autologus harvested tensor fascia lata (Fig. 5b and c). Wound explored through extended supra orbital lacerations and bony fragments were debrided, The leak was repaired with fascia lata and fibrin glue, gel foam packing was given and wound was closed in layers (Fig. 5d)
Post operatively, patient's general condition improved and CSF leak stopped 48 h after the surgery. Two months post trauma, the right eye was within normal limits. The left eye had nil perception of light, the cornea continued to be avascular and hazy, and the eye was pre phthisical. The conjunctiva re epithelized and the ocular motility was restored in all quadrants except abduction. Left lower lid laceration had a wound dehiscence and the patient was scheduled for a secondary correction (Fig. 6a and b).
Jump in the discussion.
No email address required.
More options
Context
God damn, glad hes alive at least
Jump in the discussion.
No email address required.
More options
Context
Jump in the discussion.
No email address required.
More options
Context